Program for Multi Level Inheritance and Function Overriding:
Function overriding is a very key programming feature in OOP system. This allows programmers to create objects which has similar function ( with same name) but having different implementations. Such technique is really helpful in situations where each object has a common function but implementations ( games for example).
Multi Level Inheritance:
In this type of inheritance one class inherits B inherits a base class A. After that B acts as a base class for next class C. So B inherits A, C inherits B.
in this example we have a base class "animal".
The next class "Tiger" inherits "animal".
Then "SaberTooth" inherits "Tiger".
Both Tiger and SaberTooth get the functionality of Base class Animal.
Function Overriding:
This is the feature that can change the behaviour of inherited function in derived class. Here we will change the inherited function "attack()". Note that overridden function may have completely different functioning then original
Code:
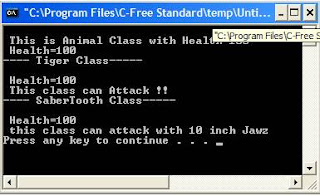
output:
Function overriding is a very key programming feature in OOP system. This allows programmers to create objects which has similar function ( with same name) but having different implementations. Such technique is really helpful in situations where each object has a common function but implementations ( games for example).
Multi Level Inheritance:
In this type of inheritance one class inherits B inherits a base class A. After that B acts as a base class for next class C. So B inherits A, C inherits B.
in this example we have a base class "animal".
The next class "Tiger" inherits "animal".
Then "SaberTooth" inherits "Tiger".
Both Tiger and SaberTooth get the functionality of Base class Animal.
Function Overriding:
This is the feature that can change the behaviour of inherited function in derived class. Here we will change the inherited function "attack()". Note that overridden function may have completely different functioning then original
Code:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; //--Our base class class animal { public: int life;// base class has an attribute that will get passed to derived classes animal() { life=100; } void say() { cout<<"\n This is Animal Class with Health="<<life; } void showHealth() { cout<<"\n Health="<<life; } }; //---Tiger class inherits animal class so gets all his public members: //---life //--say() //---showHealth() class Tiger : public animal { public: Tiger() { } void attack() { cout<<"\n This class can Attack !!"; } }; //--this class inherits tiger class also gets his public members: //--attack() //--this class has its own member data bigFangs //--this also overrrides the inherited attack function class SaberTooth : public Tiger { public: int bigFangs; SaberTooth() { bigFangs=10; } // redefining inherited method will overrride it void attack() { cout<<"\n this class can attack with "<<bigFangs<<" inch Jawz\n"; } }; int main() { animal a; a.say(); a.showHealth(); cout<<"\n---- Tiger Class-----\n"; Tiger t; t.showHealth();// <--gets it from animal class t.attack();//<--its own cout<<"\n---- SaberTooth Class-----\n"; SaberTooth s; s.showHealth();//<--from base class to tiger then to this s.attack();//<--Overrrided method }
output: